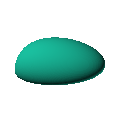
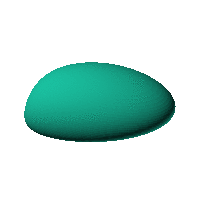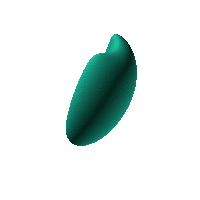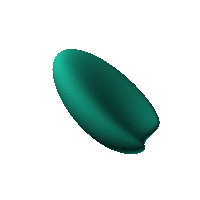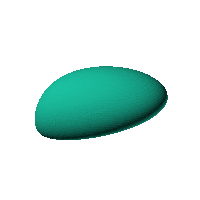
The blob in all its glory:
 Twirl with your mouse
Twirl with your mouse
This is aimed at being a case that has an obvious way of sitting on a surface and a recessed area for a hole for a USB or other cable. The formula was generated in Mathematica but GNU Octave was used to generate an STL file from the formula.
|
Click on the snapshot to download the blob's stl file.
|
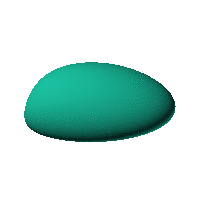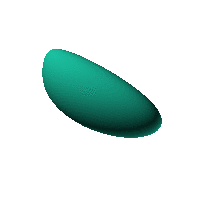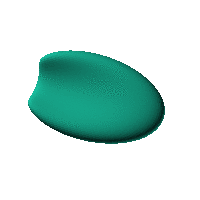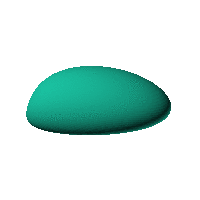
|
Octave Code:
# name of the blob
project = "blob67";
# function at origin must be <0, and >0 far enough away. w=0 defines the surface
function w = f(x2,y2,z2,c,r) # three lobed toroid with low profile bumps and flat top
x = (x2-c(1))/r(1);
y = (y2-c(2))/r(2);
z = (z2-c(3))/r(3);
w = 3.5*(7.14286.*x.^2+(-4.28571).*x.^3+x.^4+( ...
-4.28571).*x.^2.*z+7.14286.*z.^2+(-17.1429).*x.*z.^2+ ...
8.0.*x.^2.*z.^2+(-17.1429).*z.^3+16.0.*z.^4+2.03175.* ...
y.^2+(-17.1429).*x.*y.^2+8.*x.^2.*y.^2+(-17.1429).*z.* ...
y.^2+32.0.*z.^2.*y.^2+16.0.*y.^4);
endfunction;
step = 2; # grid pitch in mm start with 4mm to see the shape quickly. Once you have it just right, change to 2mm for printing
c_outer = [-10,0,-40]; # for moving center (origin) of blob
r_outer = [70,70,70];# for scaling blob
xmin = 0 ; # avoid the origin because the inverse of the gradient is NaN there
xmax = 250 ;
source("../octave/func2stl_v01.m"); # do all the calculations
GNU Octave


 Twirl with your mouse
Twirl with your mouse

